250x250
Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
Tags
- fnmatch
- shuffle()
- decode()
- inplace()
- fileinput
- remove()
- __annotations__
- items()
- __getitem__
- MySqlDB
- MySQL
- CSS
- choice()
- __sub__
- glob
- randrange()
- node.js
- locals()
- View
- discard()
- mro()
- __len__
- HTML
- Database
- JS
- count()
- 오버라이딩
- zipfile
- shutil
- 파이썬
Archives
- Today
- Total
흰둥이는 코드를 짤 때 짖어 (왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!왈!)
(Python) 파이토치 본문
728x90
반응형
1. 파이토치(Pytorch)
- 텐서플로우와 함께 머신러닝, 딥러닝에서 가장 널리 사용되는 프레임워크
- 초기에는 Torch라는 이름으로 Lua언어 기반으로 만들어졌으나, 파이썬 기반으로 변경한 것이 Pytorch
- 뉴욕대학교와 페이스북이 공동으로 개발하였고, 현재 가장 대중적이고 널리 사용됨
In [ ]:
import torch
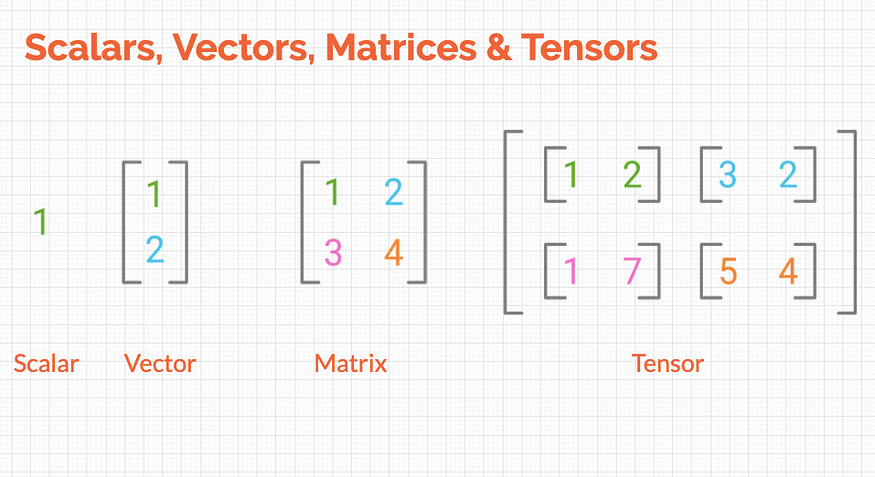
print(torch.__version__)2.0.1+cu1181-1. 스칼라(Scalar)
- 하나의 상수를 의미
In [ ]:
var1 = torch.tensor([1])In [ ]:
type(var1)Out[ ]:
torch.TensorIn [ ]:
var2 = torch.tensor([6.5])In [ ]:
# 두 스칼라의 사칙 연산
print(var1 + var2)
print(var1 - var2)
print(var1 * var2)
print(var1 / var2)tensor([7.5000])
tensor([-5.5000])
tensor([6.5000])
tensor([0.1538])1-2. 벡터(Vector)
- 상수가 두 개 이상 나열되었을 경우
In [ ]:
vector1 = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
vector1Out[ ]:
tensor([1, 2, 3])In [ ]:
vector2 = torch.tensor([10, 20, 30])In [ ]:
# 두 벡터의 사칙 연산
print(vector1 + vector2)
print(vector1 - vector2)
print(vector1 * vector2)
print(vector1 / vector2)tensor([11, 22, 33])
tensor([ -9, -18, -27])
tensor([10, 40, 90])
tensor([0.1000, 0.1000, 0.1000])1-3. 행렬(Matrix)
- 2개 이상의 벡터 값을 가지고 만들어진 값으로 행과 열의 개념을 가진 숫자의 나열
In [ ]:
matrix1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(matrix1)tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])In [ ]:
matrix2 = torch.tensor([[7, 8], [9, 10]])
print(matrix2)tensor([[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]])In [ ]:
# 두 행렬의 사칙 연산
print(matrix1 + matrix2)
print(matrix1 - matrix2)
print(matrix1 * matrix2)
print(matrix1 / matrix2)tensor([[ 8, 10],
[12, 14]])
tensor([[-6, -6],
[-6, -6]])
tensor([[ 7, 16],
[27, 40]])
tensor([[0.1429, 0.2500],
[0.3333, 0.4000]])1-4. 텐서(Tensor)
- 다수의 행렬이 모이면 텐서라고 부름
- 배열이나 행렬과 매우 유사한 특수 자료구조
- 파이토치는 텐서를 사용하여 모델의 입력과 출력, 모델의 매개변수들을 처리 사용됨
In [ ]:
from IPython.display import Image
Image(url='https://miro.medium.com/max/875/1*jRyyMAhS_NZxqyv3EoLCvg.png')Out[ ]:
In [ ]:
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
print(tensor1)tensor([[[1, 2],
[3, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])In [ ]:
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[[9, 10], [11, 12]], [[13, 14], [15, 16]]])
print(tensor2)tensor([[[ 9, 10],
[11, 12]],
[[13, 14],
[15, 16]]])In [ ]:
print(tensor1 + tensor2)
print(tensor1 - tensor2)
print(tensor1 * tensor2)
print(tensor1 / tensor2)tensor([[[10, 12],
[14, 16]],
[[18, 20],
[22, 24]]])
tensor([[[-8, -8],
[-8, -8]],
[[-8, -8],
[-8, -8]]])
tensor([[[ 9, 20],
[ 33, 48]],
[[ 65, 84],
[105, 128]]])
tensor([[[0.1111, 0.2000],
[0.2727, 0.3333]],
[[0.3846, 0.4286],
[0.4667, 0.5000]]])In [ ]:
print(torch.add(tensor1, tensor2))
print(torch.subtract(tensor1, tensor2))
print(torch.multiply(tensor1, tensor2))
print(torch.divide(tensor1, tensor2))
print(torch.matmul(tensor1, tensor2)) # 행렬곱tensor([[[10, 12],
[14, 16]],
[[18, 20],
[22, 24]]])
tensor([[[-8, -8],
[-8, -8]],
[[-8, -8],
[-8, -8]]])
tensor([[[ 9, 20],
[ 33, 48]],
[[ 65, 84],
[105, 128]]])
tensor([[[0.1111, 0.2000],
[0.2727, 0.3333]],
[[0.3846, 0.4286],
[0.4667, 0.5000]]])
tensor([[[ 31, 34],
[ 71, 78]],
[[155, 166],
[211, 226]]])In [ ]:
print(tensor1.add_(tensor2)) # tensor1에 결과를 다시 저장, 모든 사칙연산자에 _를 붙여 사용할 수 있
print(tensor1)tensor([[[10, 12],
[14, 16]],
[[18, 20],
[22, 24]]])Out[ ]:
tensor([[[10, 12],
[14, 16]],
[[18, 20],
[22, 24]]])2. 텐서의 변환
In [ ]:
data = [[1, 2], [3, 4]]
print(data)[[1, 2], [3, 4]]In [ ]:
x_data = torch.tensor(data)
print(x_data)tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])In [ ]:
import numpy as npIn [ ]:
np_array = np.array(data)
np_arrayOut[ ]:
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])In [ ]:
x_np_1 = torch.tensor(np_array)
x_np_1Out[ ]:
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])In [ ]:
x_np_1[0, 0] = 100
print(x_np_1)
print(np_array)tensor([[100, 2],
[ 3, 4]])
[[1 2]
[3 4]]In [ ]:
x_np_2 = torch.as_tensor(np_array) # ndarray와 동일한 메모리 주소를 가리키는 뷰를 만드는 함수(잘 사용 안함)
print(x_np_2)
x_np_2[0, 0] = 200 # 기존 메모리 주소의 ndarray값을 변경하게 됨
print(x_np_2)
print(np_array)tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
tensor([[200, 2],
[ 3, 4]])
[[200 2]
[ 3 4]]In [ ]:
x_np_3 = torch.from_numpy(np_array) # ndarray와 동일한 메모리 주소를 가리키는 뷰를 만드는 함수(잘 사용 안함)
print(x_np_3)
x_np_3[0, 0] = 400 # 기존 메모리 주소의 ndarray값을 변경하게 됨
print(x_np_3)
print(np_array)tensor([[200, 2],
[ 3, 4]])
tensor([[400, 2],
[ 3, 4]])
[[400 2]
[ 3 4]]In [ ]:
np_again = x_np_1.numpy()
print(np_again, type(np_again))[[100 2]
[ 3 4]] <class 'numpy.ndarray'>3. 파이토치 주요 함수
In [ ]:
a = torch.ones(2, 3)
print(a)tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])In [ ]:
b = torch.zeros(2, 3)
print(b)tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])In [ ]:
c = torch.full((2, 3), 10)
print(c)tensor([[10, 10, 10],
[10, 10, 10]])In [ ]:
d = torch.empty(2, 3)
print(d)tensor([[2.3516e+17, 4.5684e-41, 2.3516e+17],
[4.5684e-41, 4.4842e-44, 0.0000e+00]])In [ ]:
e = torch.eye(5)
print(e)tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])In [ ]:
f = torch.arange(10)
print(f)tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])In [ ]:
g = torch.rand(2, 3)
print(g)tensor([[0.8452, 0.5497, 0.4099],
[0.8343, 0.4671, 0.2026]])In [ ]:
h = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(h)tensor([[-0.5985, 1.3681, -0.6921],
[ 1.2127, 1.2016, -0.9689]])In [ ]:
i = torch.arange(16).reshape(2, 2, 4)
print(i, i.shape)
# 차원을 인덱스로 변경
j = i.transpose(1, 2) # 2, 4, 2
print(j, j.shape)tensor([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7]],
[[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15]]]) torch.Size([2, 2, 4])
tensor([[[ 0, 4],
[ 1, 5],
[ 2, 6],
[ 3, 7]],
[[ 8, 12],
[ 9, 13],
[10, 14],
[11, 15]]]) torch.Size([2, 4, 2])In [ ]:
# 차원을 인덱스로 변경
k = i.permute((2, 0, 1)) # 2, 2, 4 -> 4, 2, 2
print(k, k.shape)tensor([[[ 0, 4],
[ 8, 12]],
[[ 1, 5],
[ 9, 13]],
[[ 2, 6],
[10, 14]],
[[ 3, 7],
[11, 15]]]) torch.Size([4, 2, 2])4. GPU 사용하기
- 코랩에서 device 변경하는 방법
- 상단 메뉴 -> 런타임 -> 런타임 유형변경 -> 하드웨어 가속기를 GPU로 변경 -> 저장 -> 다시 시작 및 모두 실행
In [ ]:
tensor = torch.rand(3, 4)
print(f'shape: {tensor.shape}')
print(f'type: {tensor.dtype}')
print(f'device: {tensor.device}')shape: torch.Size([3, 4])
type: torch.float32
device: cpuIn [ ]:
tensor = tensor.reshape(4, 3)
tensor = tensor.int()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print('GPU를 사용할 수 있음')
tensor = tensor.to('cuda')
print(f'shape: {tensor.shape}')
print(f'type: {tensor.dtype}')
print(f'device: {tensor.device}')GPU를 사용할 수 있음
shape: torch.Size([4, 3])
type: torch.int32
device: cuda:05. 텐서의 인덱싱과 슬라이싱
In [ ]:
a = torch.arange(1, 13).reshape(3, 4)
print(a)tensor([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12]])In [ ]:
print(a[1])
print(a[0, -1])
print(a[1:-1])
print(a[:2, 2:])tensor([5, 6, 7, 8])
tensor(4)
tensor([[5, 6, 7, 8]])
tensor([[3, 4],
[7, 8]])728x90
반응형
'파이썬 머신러닝, 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Python) 파이토치로 구현한 논리 회귀 (0) | 2023.06.15 |
|---|---|
| (Python) 파이토치로 구현한 선형회 (0) | 2023.06.15 |
| (Python) KMeans (1) | 2023.06.15 |
| (Python) lightGBM (0) | 2023.06.15 |
| (Python) 랜덤 포레스트 (0) | 2023.06.15 |
Comments




